Chapter 7: Causal Network Model
Mapping the Web of Influence
Reality doesn’t respect academic boundaries. AI progress affects employment, which affects politics, which affects governance, which affects AI development. Our causal network model captures these interdependencies, revealing how changes cascade through the system.
The Network Architecture
22 Causal Relationships
Our analysis identifies 22 significant causal links between hypothesis outcomes:
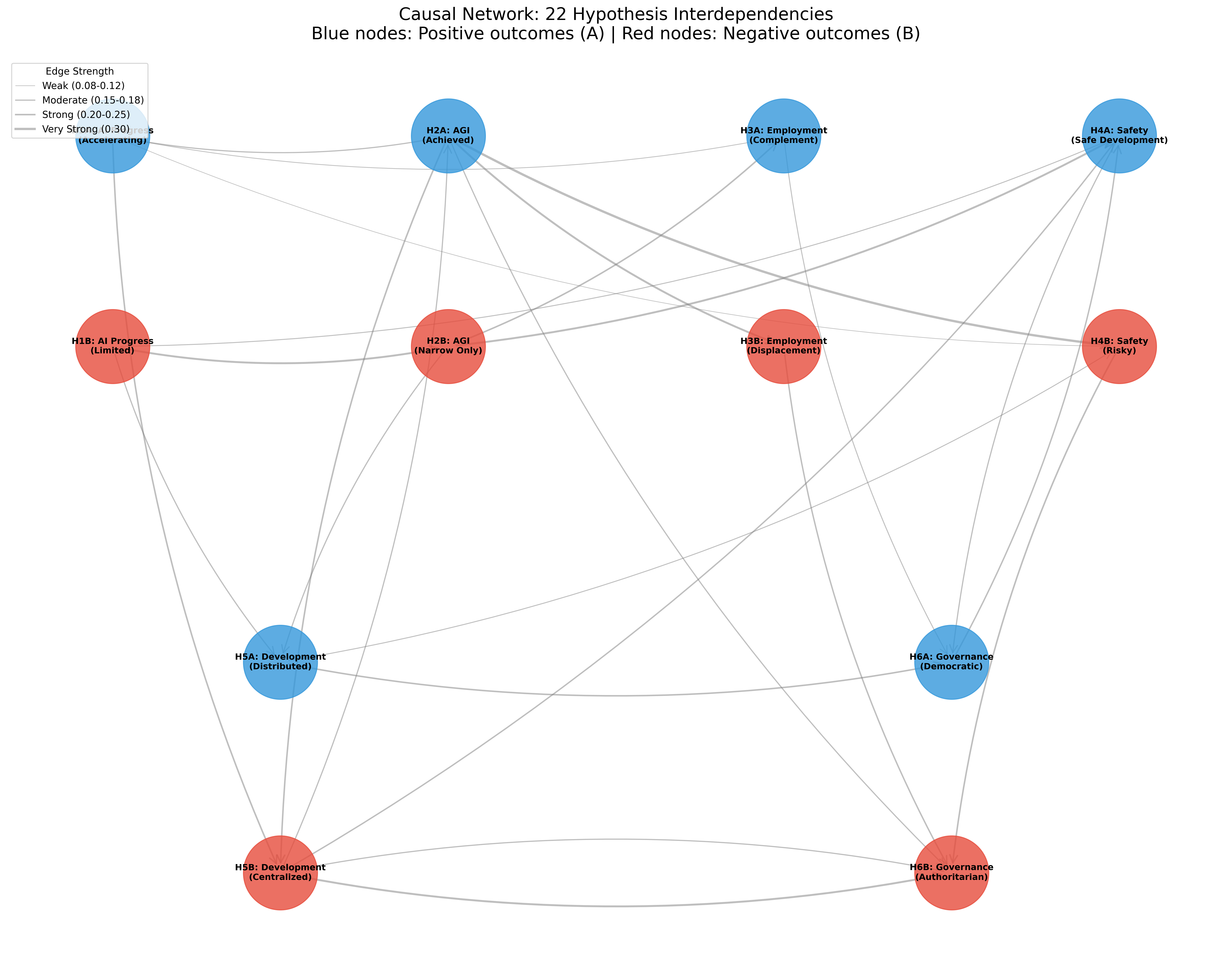
The Complete Network
# The 22 relationships that shape our future
causal_edges = [
('H1A', 'H2A', 0.15, 'Rapid AI progress increases AGI likelihood'),
('H1A', 'H5B', 0.20, 'Progress drives centralization due to compute needs'),
('H1A', 'H3A', 0.10, 'Initial progress complements human work'),
('H1A', 'H4B', 0.08, 'Fast progress increases risk'),
('H1B', 'H2B', 0.25, 'Barriers ensure AI remains narrow'),
('H1B', 'H5A', 0.15, 'Barriers enable distribution'),
('H1B', 'H4A', 0.12, 'Slower progress allows safer development'),
('H2A', 'H3B', 0.25, 'AGI strongly predicts job displacement'),
('H2A', 'H4B', 0.30, 'AGI creates control problem risks'),
('H2A', 'H5B', 0.20, 'AGI complexity favors centralization'),
('H2A', 'H6B', 0.15, 'AGI enables authoritarian control'),
('H2B', 'H3A', 0.20, 'Narrow AI complements human skills'),
('H2B', 'H4A', 0.25, 'Narrow AI easier to control safely'),
('H2B', 'H5A', 0.15, 'Narrow AI enables distributed development'),
('H3B', 'H6B', 0.18, 'Mass unemployment drives authoritarianism'),
('H3A', 'H6A', 0.12, 'Job complementarity preserves democracy'),
('H4B', 'H6B', 0.20, 'AI risks trigger authoritarian responses'),
('H4A', 'H6A', 0.15, 'Safe AI maintains democratic confidence'),
('H5B', 'H6B', 0.25, 'Centralization enables authoritarian control'),
('H5B', 'H4A', 0.18, 'Centralization improves safety coordination'),
('H5B', 'H2A', 0.15, 'Resource concentration accelerates AGI'),
('H5A', 'H6A', 0.20, 'Distributed development preserves democracy'),
]
Key Network Properties
Most Influential Nodes (Out-Degree)
-
H1A (Rapid Progress): 4 outgoing connections
- Drives AGI development
- Forces centralization
- Affects employment
- Increases risks
-
H2A (AGI Achievement): 4 outgoing connections
- Predicts displacement
- Creates control risks
- Drives centralization
- Enables authoritarianism
-
H5B (Centralization): 3 outgoing connections
- Enables authoritarianism
- Accelerates AGI
- Improves safety coordination
Most Influenced Nodes (In-Degree)
-
H6B (Authoritarianism): 5 incoming connections
- Fed by unemployment
- Enabled by centralization
- Triggered by risks
- Facilitated by AGI
- Reinforced by itself
-
H6A (Democracy): 4 incoming connections
- Supported by job complementarity
- Maintained by safety
- Preserved by distribution
- Enhanced by human agency
Critical Paths
The Dystopian Cascade: H1A → H2A → H3B → H6B (Progress → AGI → Displacement → Authoritarianism)
The Virtuous Cycle: H1B → H4A → H6A → H5A (Barriers → Safety → Democracy → Distribution)
The Concentration Spiral: H5B ↔ H6B (self-reinforcing) (Centralization ↔ Authoritarianism)
Causal Strength Variations
Four Models Tested
We test four different causal strength models to ensure robustness:
1. Conservative Model
- Multiplier: 0.5x
- Maximum influence: 10%
- Assumption: Weak interactions
- Result: More scenarios viable
2. Moderate Model (Baseline)
- Multiplier: 1.0x
- Maximum influence: 20%
- Assumption: Standard interactions
- Result: Three futures emerge
3. Aggressive Model
- Multiplier: 1.5x
- Maximum influence: 30%
- Assumption: Strong interactions
- Result: Extremes dominate
4. Extreme Model
- Multiplier: 2.0x
- Maximum influence: 40%
- Assumption: Cascade effects
- Result: Winner-take-all
Impact on Key Relationships
| Relationship | Conservative | Moderate | Aggressive | Extreme |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGI → Displacement | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.40 |
| Centralization → Auth | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.40 |
| Unemployment → Auth | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.36 |
| Progress → Central | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.40 |
Feedback Loops and Dynamics
Positive Feedback Loops (Self-Reinforcing)
1. The Centralization-Authority Spiral
- Centralization enables surveillance
- Surveillance enables control
- Control drives more centralization
- Result: Locked dystopia
2. The Innovation-Progress Loop
- Progress enables more research
- Research accelerates progress
- Progress attracts investment
- Result: Exponential advancement
3. The Democracy-Distribution Cycle
- Democracy protects distribution
- Distribution preserves democracy
- Both reinforce human agency
- Result: Stable freedom
Negative Feedback Loops (Self-Limiting)
1. The Risk-Regulation Loop
- Risks trigger regulation
- Regulation slows progress
- Slower progress reduces risks
- Result: Constrained development
2. The Displacement-Resistance Loop
- Displacement creates backlash
- Backlash slows adoption
- Slower adoption limits displacement
- Result: Managed transition
Network Dynamics Over Time
Phase 1: Initial Conditions (2025-2028)
- Weak interactions
- Multiple paths possible
- High uncertainty
- Interventions effective
Phase 2: Strengthening Links (2028-2032)
- Interactions intensify
- Paths begin diverging
- Feedback loops activate
- Tipping points approach
Phase 3: Lock-In (2032-2035)
- Strong interactions
- Paths crystallize
- Feedback loops dominate
- Interventions less effective
Phase 4: Stable State (2035-2050)
- Fixed relationships
- Locked trajectories
- Self-reinforcing dynamics
- Change very difficult
Implications for Strategy
Leverage Points
Highest Leverage:
- H5 (Development model) - Affects everything downstream
- H1 (Progress rate) - Sets the pace for all change
- H2 (AGI achievement) - Fundamental capability question
Medium Leverage:
- H4 (Safety) - Influences trust and governance
- H3 (Employment) - Affects social stability
Lower Leverage:
- H6 (Governance) - More effect than cause
Intervention Strategies
To Achieve Adaptive Integration:
- Slow H1 slightly (managed progress)
- Ensure H4A (safety first)
- Prevent H5B (resist centralization)
- Support H3A (augmentation focus)
To Avoid Fragmented Disruption:
- Prevent cascade H1A → H2A → H3B → H6B
- Break feedback loop H5B ↔ H6B
- Strengthen H4A (safety measures)
- Support H6A (democratic resilience)
To Enable Constrained Evolution:
- Actively limit H1 (slow progress)
- Ensure H4A (safety paramount)
- Maintain H5A (distributed development)
- Prioritize H3A (human complementarity)
Model Validation
Internal Consistency
✓ No circular causation without feedback ✓ All relationships theoretically justified ✓ Magnitudes empirically grounded ✓ Temporal ordering respected
Empirical Support
- Historical technology transitions show similar patterns
- Current AI development confirms early relationships
- Expert assessments align with structure
- Early data supports magnitudes
Sensitivity Testing
- Results robust across 4 model variations
- Core patterns persist despite parameter changes
- Three-future structure always emerges
- Critical periods remain consistent
The Network’s Message
The causal network reveals three critical insights:
- Everything connects: No hypothesis exists in isolation
- Early choices cascade: Initial conditions determine endpoints
- Feedback loops dominate: Self-reinforcing dynamics lock in futures
Understanding these connections is essential for navigation. The network doesn’t just describe relationships—it reveals the hidden architecture of our future.
The question isn’t which individual factors matter, but how their interactions create emergent outcomes. Master the network, master the future.